“`html
Effective Ways to Master Keto Enol Tautomerism in 2025
Keto enol tautomerism is an essential concept in organic chemistry, involving the equilibrium between two structural forms: the keto form and the enol form. As the chemistry world evolves, especially in synthetic applications and metabolic pathways, understanding the principles of keto enol tautomerism, such as tautomeric equilibrium and reaction kinetics, allows chemists to optimize reactions and develop new methodologies. This article will address practical techniques, applications, and insights to master keto enol tautomerism effectively in 2025.
Understanding Tautomeric Equilibrium
The **tautomeric equilibrium** is vital for chemists, as it underscores the dynamic conversion between keto and enol forms. In this equilibrium, the position and stability of each tautomer play pivotal roles in determining the outcome of reactions involving **carbonyl compounds**. The keto form tends to be more stable due to resonance and lower energy, thus predominating in the equilibrium mixture for many **carbonyl compounds**. However, **enolate ions** can form under specific conditions, facilitating the conversion to the enol phase. It’s crucial to consider factors such as sterics and electronic effects when analyzing the stability of these two forms during experimental observations.
The Mechanism of Keto-Enol Tautomerization
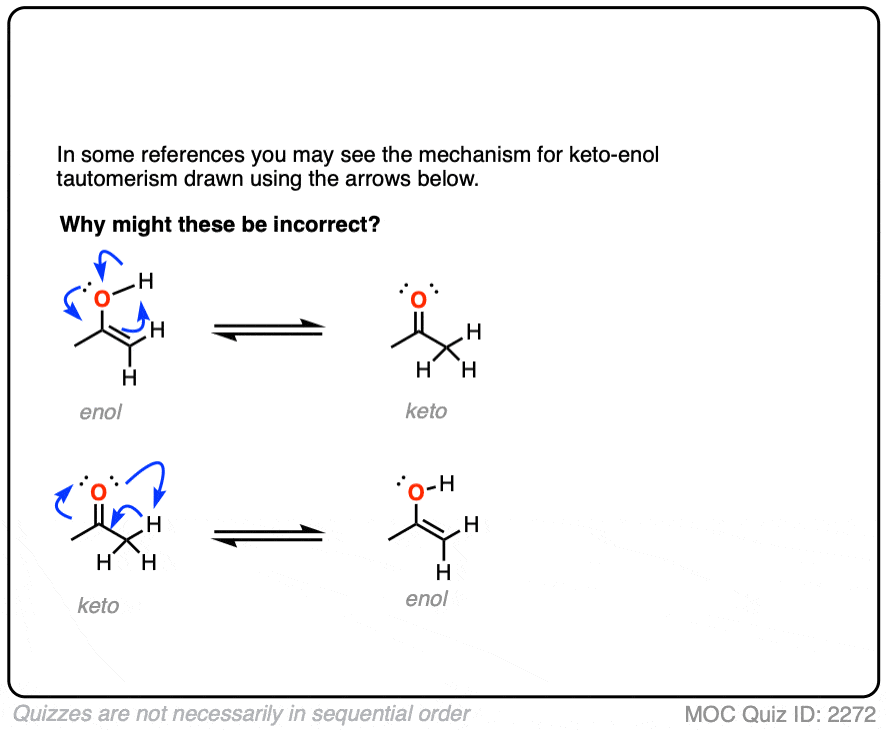
The **keto-enol tautomerization mechanism** typically involves reversible proton transfer. Understanding this step is essential for predicting reaction pathways. For instance, proton transfer from the α-hydrogen of the ketone leads to the formation of an **enolate** intermediate, particularly in basic conditions. Conversely, acid-catalyzed tautomerization may occur upon electrophilic attack followed by rapid protonation to yield the enol. Recognizing how **acid-base catalysis** influences these pathways enables chemists to manipulate reaction conditions effectively for desired outcomes in organic synthesis.
Thermodynamic Stability of Tautomeric Forms
The thermodynamic stability between the keto and enol forms is not just a theoretical concept, but a practical consideration when conducting organic reactions. Typically, the **stability hierarchy** favors the keto form; however, factors such as solvent effects and substitution can alter this balance. Variations in **polarity effects** and solvation can impact the equilibrium constant, shifting the ratio of enol to keto forms. Understanding these influences can guide chemists in optimizing conditions, such as selecting an aprotic polar solvent, to either stabilize the keto form or facilitate **keto-enol interconversion** effectively.
Techniques for Investigating Keto-Enol Tautomerization
Employing various techniques for studying **keto-enol tautomerization** provides valuable insights into chemical reactivity and stability. Among these, spectral analysis through methods like IR spectroscopy and NMR analysis allows researchers to evaluate tautomeric distributions and kinetics of interconversion. **Tautomerization spectroscopy** is particularly helpful in detecting subtle shifts in tautomeric ratios which may be crucial in optimizing reactions in synthetic chemistry. These analytical tools help establish a clearer understanding of **reaction intermediates** and pathways encountered during tautomerization studies.
IR and NMR Spectroscopic Identification
The ability to differentiate and accurately identify tautomeric forms via IR and NMR spectroscopy is an invaluable skill for organic chemists. For instance, the characteristic peaks observed in IR spectroscopy can indicate the presence of hydroxyl groups in the **enol form**. Detailed NMR spectra further reveal the variations in chemical shifts corresponding to the environment of protons and carbons in both forms. Utilizing **spectroscopic identification** techniques allows chemists to confirm the presence and stability of each tautomer under various reaction conditions, enhancing their understanding of reaction kinetics.
Experimental Techniques to Explore Tautomerism
Implementing experimental techniques is crucial in unraveling the complexities of **keto-enol tautomerization**. Lab techniques, such as utilizing **reaction kinetics** to measure the rates of tautomerization under different pH conditions or by assessing **solvent effects** on equilibration, can elucidate factors that govern tautomer stability and interconversion. Moreover, adopting **educational resources** focused on experimental design can foster a deeper understanding of these phenomena among budding chemists, emphasizing the practical applications in everyday synthetic scenarios.
Keto-Enol Tautomerism in Biological Systems
The relevance of keto enol tautomerism extends into the realm of biology, particularly in understanding metabolic pathways. Many biochemical processes depend on the existence of these tautomers, influencing mechanisms like glucose metabolism or the functioning of **tautomerase enzymes**. Analyzing how these enzymatic reactions benefit from the dynamic nature inherent in tautomeric forms can shed light on enzymatic efficiency and specificity. Hence, research into this area further contributes to the broader implications of keto-enol tautomerism in biological systems.
Impact on Metabolic Pathways
The role of **keto-enols in biology** can be exemplified through their involvement in metabolic pathways, where the equilibrium between these forms can affect the pathways’ efficiency and the yields of crucial intermediates. An outbreak of **keto enol tautomerism** can dictate the engagement and effectiveness of enzymes, providing a prime example in pharmaceutical applications. Comprehending these interactions can spur further advancements in drug design, as knowing the **tautomeric behavior** aids in predicting the pharmacokinetics and dynamics of various therapeutic agents.
Applications in Synthesis and Drug Design
In the sphere of synthetic chemistry, **keto-enol tautomerism** holds considerable importance, especially in the design of novel compounds through direct applications in synthesis. Understanding the unique properties of the **keto** and **enol forms** can guide the successful creation of organic intermediates, promoting efficiency in **organic synthesis**. Specifically, insights gained parallelly enhance the design of target molecules that leverage **keto enol ratios** for stability or entropic favorability in complex biological systems.
Key Takeaways
- The concepts of keto enol tautomerism are crucial in both theoretical and applied chemistry.
- Understanding tautomeric equilibrium helps chemists predict the stability and reactivity of carbonyl compounds and their derivatives.
- Advanced analytical techniques such as IR and NMR spectroscopy are fundamental in exploring tautomeric forms.
- Decoding the role of keto-enol tautomerism in biological systems provides insights that bridge organic synthesis with metabolic pathways.
- Practical applications of keto-enol interconversion pave the way for innovative materials and pharmaceuticals that harness these dynamic equilibria.
FAQ
1. What is keto-enol tautomerism?
Keto-enol tautomerism refers to the chemical equilibrium established between a keto compound (carbonyl form) and its corresponding enol form (hydroxyl form). This dynamic process includes proton transfer, allowing these structural isomers to interconvert and can be influenced by factors like solvent polarity and acidity. It’s crucial for various reactions in organic synthesis and can also affect biochemical pathways.
2. What factors influence the stability of keto and enol forms?
Factors influencing **keto-enol tautomerism** include solvation effects, steric hindrance, and electronic factors such as resonance stabilization. The **equilibrium constant** of the two tautomers varies with substituents and functional groups affecting their thermodynamic stability and hence their likelihood of existing in either form during reactions.
3. How is tautomerism significant in drug design?
In drug design, understanding **keto-enol tautomerism** allows pharmaceutical chemists to optimize compound properties, predicting bioavailability and pharmacodynamics based on how these forms interact within biological systems. Tautomerism can influence the compound’s interaction with targets and enzymes, essential for drug efficacy.
4. What are the applications of IR spectroscopy in tautomerization?
**IR spectroscopy** plays a critical role in the detection and characterization of tautomeric forms. It identifies characteristic absorption peaks associated with functional groups in the keto and enol forms, providing insights into their ratios in solution. This enables chemists to better understand the dynamics of tautomerization and stability under various conditions.
5. Can keto-enol tautomerism affect chemical reactivity?
Absolutely. The predominance of the keto or enol form can significantly influence a compound’s **chemical reactivity** by affecting the accessibility of reactive sites during reactions. The effect of substituent groups can even shift tautomeric distributions, altering reaction pathways in synthetic processes.
“`